What is rare earth?
Human beings have a history of over 200 years since the discovery of rare earths in 1794. Since there were few Rare-earth mineral found at that time, only a small amount of water insoluble oxides could be obtained by chemical method. Historically, such oxides were habitually called “earth”, hence the name of rare earth.
In fact, Rare-earth mineral are not rare in nature. Rare earth is not earth, but a typical metal element. Its active type is only second to alkali metals and alkaline earth metals. They have more content in the crust than common copper, zinc, tin, cobalt, and nickel.
At present, rare earths have been widely used in various fields such as electronics, petrochemicals, metallurgy, etc. Almost every 3-5 years, scientists are able to discover new uses for rare earths, and out of every six inventions, one cannot do without rare earths.
China is rich in rare earth minerals, ranking first in three world rankings: reserves, production scale, and export volume. At the same time, China is also the only country that can provide all 17 rare earth metals, especially the medium and heavy rare earths with extremely prominent military applications.
Rare earth element composition
Rare earth elements are composed of Lanthanide elements in the periodic table of chemical elements: lanthanum (La), cerium (Ce), praseodymium (Pr), neodymium (Nd), promethium (Pm), samarium (Sm), europium (Eu), gadolinium (Gd), terbium (Tb), dysprosium (Dy), holmium (Ho), erbium (Er), thulium (Tm), ytterbium (Yb), lutetium (Lu), and two elements closely related to lanthanide: scandium (Sc) and yttrium (Y).

It is called Rare Earth, abbreviated as Rare Earth.
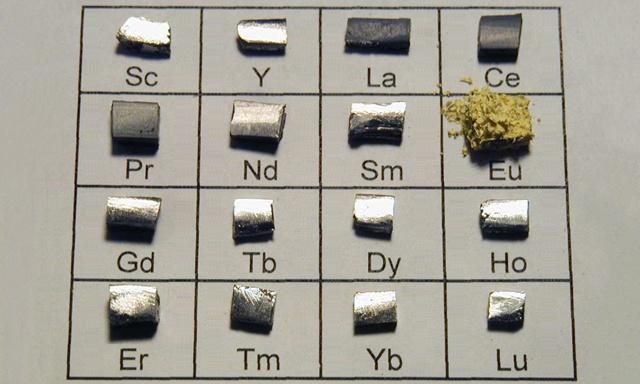
Classification of rare earth elements
Classified by the physical and chemical properties of elements:
Light rare earth elements: scandium, yttrium, lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, promethium, samarium, europium
Heavy rare earth elements: gadolinium, terbium, dysprosium, holmium, erbium, thulium, ytterbium, lutetium
Classified by mineral characteristics:
Cerium group: lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, promethium, samarium, europium
Yttrium group: gadolinium, terbium, dysprosium, holmium, erbium, thulium, ytterbium, lutetium, scandium, yttrium
Classification by extraction separation:
Light rare earth (P204 weak acidity extraction): lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium
Medium rare earth (P204 low acidity extraction): samarium, europium, gadolinium, terbium, dysprosium
Heavy rare earth (acidity extraction in P204): holmium, erbium, thulium, ytterbium, lutetium, yttrium
Properties of rare earth elements
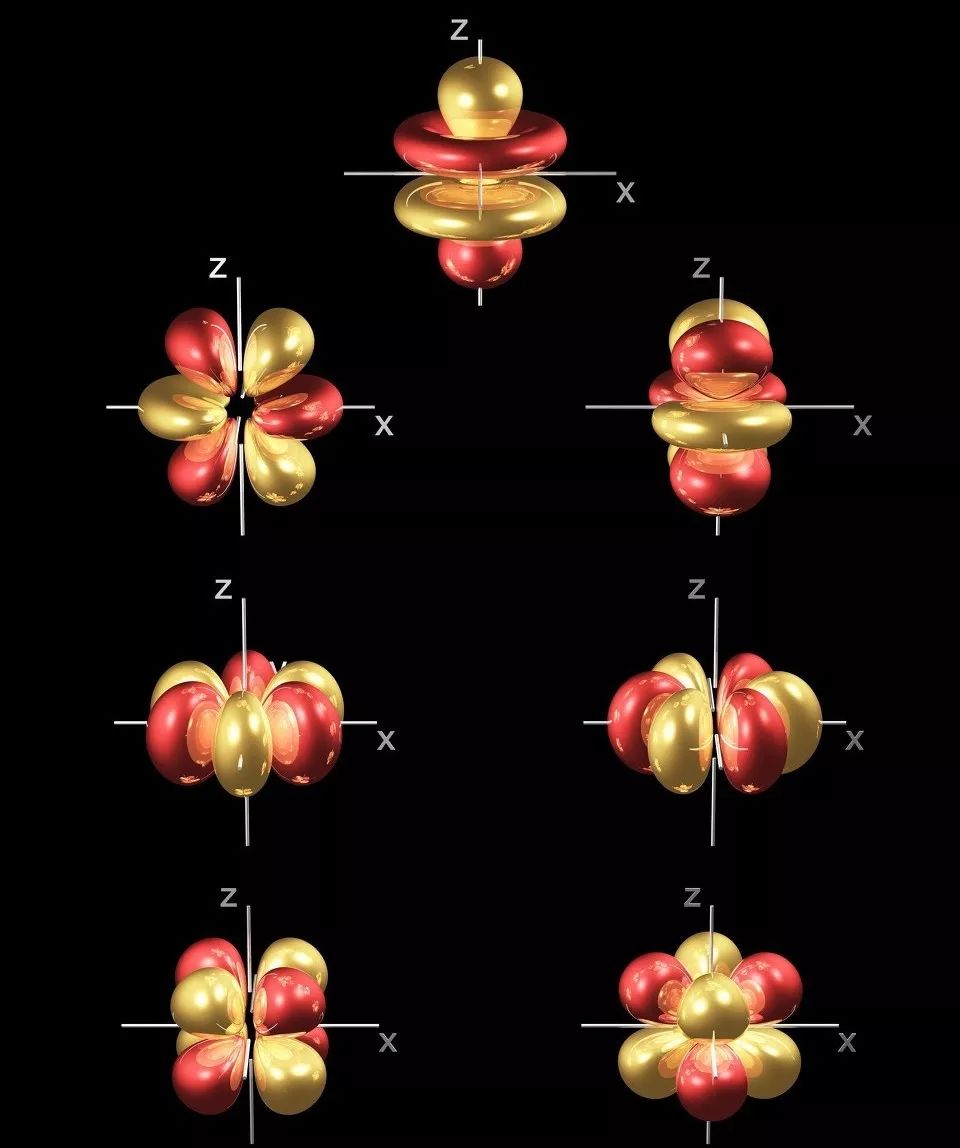
More than 50 functions of rare earth elements are related to their unique 4f electronic structure, making them widely used in both traditional materials and high-tech new materials fields.
1. Physical and chemical properties
★ Has obvious metallic properties; It is silver gray, except for praseodymium and neodymium, it appears light yellow
★ Rich oxide colors
★ Form stable compounds with non-metals
★ Metal lively
★ Easy to oxidize in the air
2 Optoelectronic properties
★ Unfilled 4f sublayer, where 4f electrons are shielded by outer electrons, resulting in various spectral terms and energy levels
When 4f electrons transition, they can absorb or emit radiation of various wavelengths from ultraviolet, visible to infrared regions, making them suitable as luminescent materials
★ Good conductivity, capable of preparing rare earth metals by electrolysis method
The Role of 4f Electrons of Rare Earth Elements in New Materials
1.Materials utilizing 4f electronic features
★ 4f electron spin arrangement: manifested as strong magnetism – suitable for use as permanent magnet materials, MRI imaging materials, magnetic sensors, superconductors, etc
★ 4f orbital electron transition: manifested as luminescent properties – suitable for use as luminescent materials such as phosphors, infrared lasers, fiber amplifiers, etc
Electronic transitions in the 4f energy level guide band: manifested as coloring properties – suitable for coloring and decolorization of hot spot components, pigments, ceramic oils, glass, etc
2 is indirectly related to 4f electron, using Ionic radius, charge and chemical properties
★ Nuclear characteristics:
Small thermal neutron Absorption cross section – suitable for use as structural materials of nuclear reactors, etc
Large neutron Absorption cross section – suitable for shielding materials of nuclear reactors, etc
★ Rare earth Ionic radius, charge, physical and chemical properties:
Lattice defects, similar Ionic radius, chemical properties, different charges – suitable for heating, catalyst, sensing element, etc
Structural specificity – suitable for use as hydrogen storage alloy cathode materials, microwave absorption materials, etc
Electro optical and dielectric properties – suitable for use as light modulation materials, transparent ceramics, etc
Post time: Jul-06-2023