
Bastnaesite
Neodymium, atomic number 60, atomic weight 144.24, with a content of 0.00239% in the crust, mainly present in monazite and bastnaesite. There are seven isotopes of neodymium in nature: neodymium 142, 143, 144, 145, 146, 148, and 150, with neodymium 142 having the highest content. With the birth of praseodymium element, neodymium element also emerged. The arrival of neodymium element has activated the rare earth field, played an important role in the rare earth field, and controlled the rare earth market.
The Discovery of Neodymium

Karl von Welsbach (1858-1929), discoverer of Neodymium
In 1885, Austrian chemist Carl Auer von Welsbach discovered neodymium in Vienna. He separated neodymium and praseodymium from symmetrical neodymium materials by separating crystalline ammonium dinitrate tetrahydrate from nitric acid, and separated them through spectral analysis. However, it was not until 1925 that they were separated in a relatively pure form.
Since the 1950s, high-purity (over 99%) neodymium has been mainly obtained through the ion exchange process of monazite. The metal itself is obtained by electrolysis of its halide salts. At present, most neodymium is extracted from Bastana stone (Ce, La, Nd, Pr) CO3F and purified through solvent extraction. Ion exchange purification is reserved for preparing the highest purity (usually>99.99%). Due to the difficulty in removing the final traces of praseodymium in the era of manufacturing relying on step-by-step crystallization technology, early neodymium glass manufactured in the 1930s had a purer purple or orange hue than modern versions.
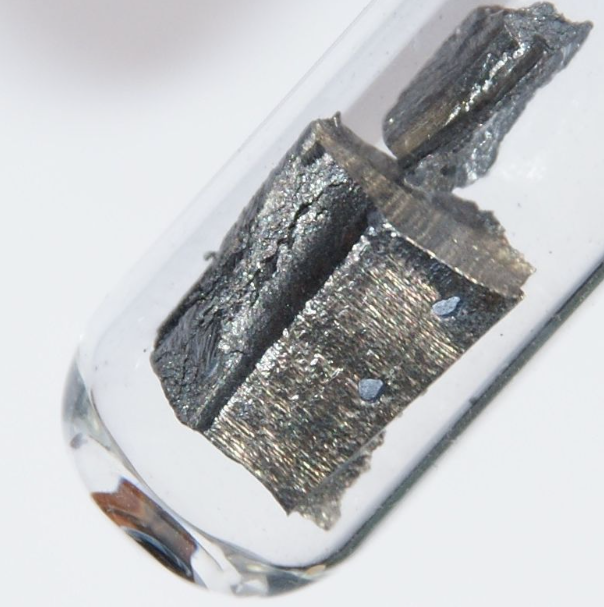
Neodymium metal has a bright silver metallic luster, a melting point of 1024 ° C, and a density of 7.004g/cm ³, It has paramagnetism. Neodymium is one of the most active rare earth metals, which rapidly oxidizes and darkens in the air, forming an oxide layer that then peels off, exposing the metal for further oxidation. Therefore, a centimeter sized neodymium sample is completely oxidized within one year. React slowly in cold water and quickly in hot water.
Neodymium electronic layout
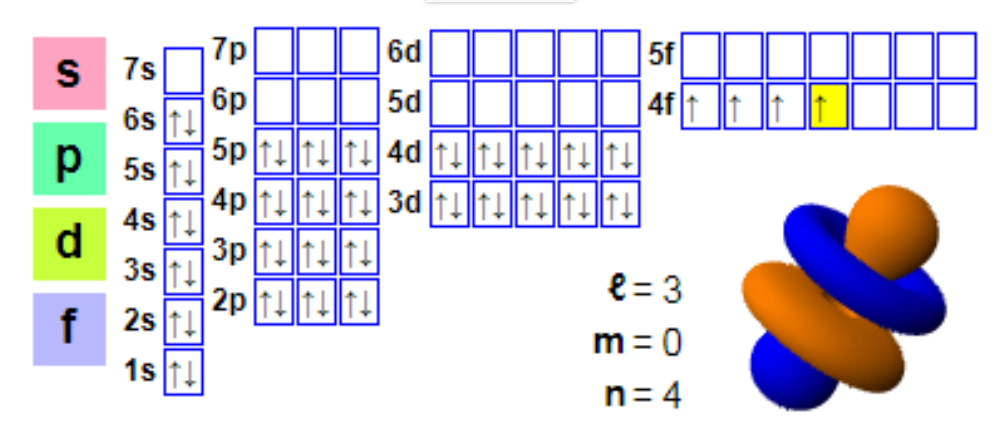
Electronic layout:
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 5s2 4d10 5p6 6s2 4f4
The laser performance of neodymium is due to the transition of 4f orbital electrons between different energy levels. This laser material is widely used in communication, information storage, medical treatment, mechanical processing, and other fields. Among them, yttrium aluminum garnet Y3Al5O12: Nd (YAG: Nd) is widely used for its excellent performance, as well as Nd doped gadolinium scandium gallium garnet with higher efficiency.
Application of neodymium
The largest user of neodymium is neodymium iron boron permanent magnet material. Neodymium iron boron magnets have a high magnetic energy product and are known as the contemporary “king of permanent magnets”. They are widely used in industries such as electronics and machinery due to their excellent performance. Francis Wall, a professor of applied mining at the Cumburn School of Mining at the University of Exeter in the UK, said: “In terms of magnets, there is really no competition with neodymium .” The successful development of the Alpha magnetic spectrometer marks that China’s various magnetic properties of neodymium iron boron magnets have reached world-class levels.
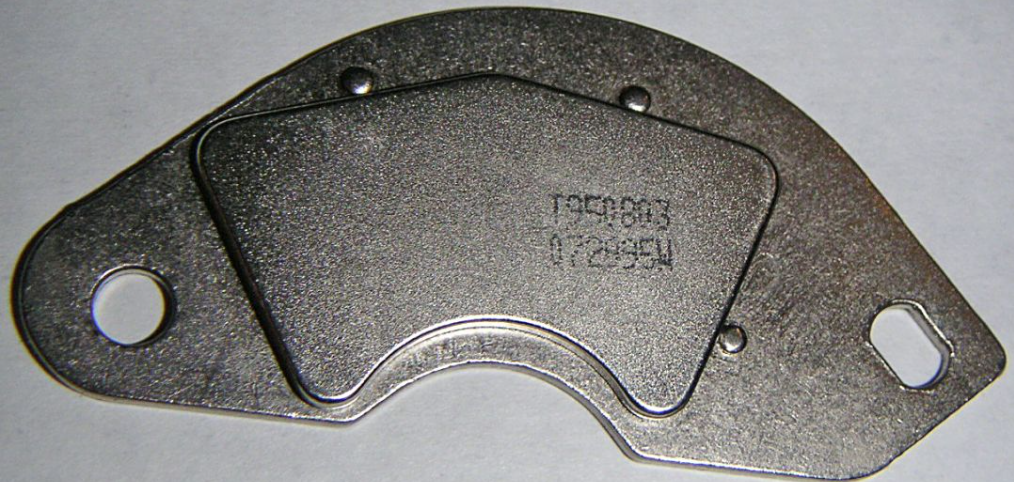

Neodymium magnet on hard disk
Neodymium can be used to manufacture ceramics, bright purple glass, artificial rubies in lasers, and special glass that can filter infrared rays. Used together with praseodymium to make goggles for glass blowing workers.
Adding 1.5% to 2.5% nano neodymium oxide to magnesium or aluminum alloys can improve the high-temperature performance, airtightness, and corrosion resistance of the alloy, and is widely used as an aerospace material.
Nanometer yttrium aluminum garnet doped with neodymium oxide generates short wave laser beams, which are widely used in industry for welding and cutting thin materials with a thickness of less than 10mm.
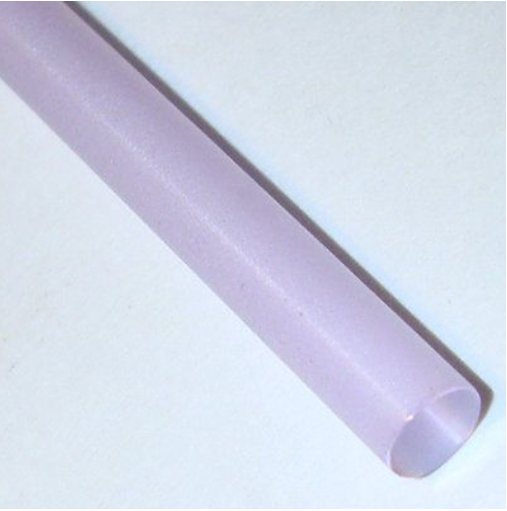

Nd: YAG laser rod
In medical practice, nano yttrium aluminum garnet lasers doped with nano High Purity 99.9% Neodymium Oxide CAS No 1313-97-9 (epomaterial.com)are used instead of surgical knives to remove surgical or disinfect wounds.
Neodymium glass is made by adding neodymium oxide to the glass melt. Usually, lavender appears on neodymium glass under sunlight or incandescent light, but it appears light blue under fluorescent lighting. Neodymium can be used to color delicate shades of glass such as pure violet, burgundy, and warm gray.
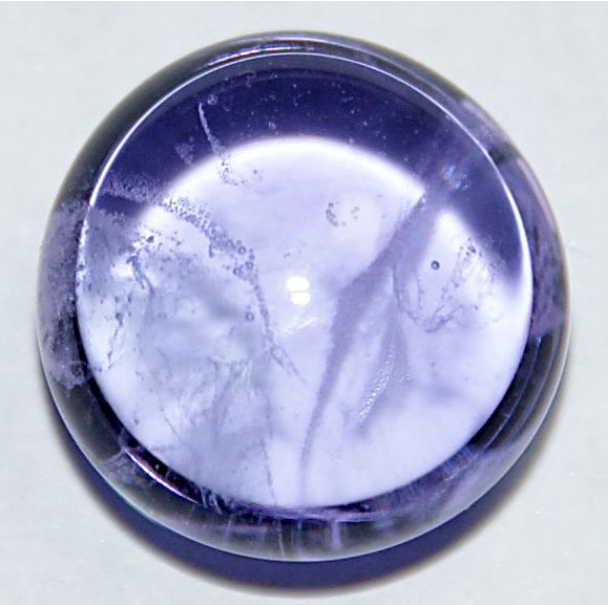

Neodymium glass
With the development of science and technology and the expansion and extension of rare earth technology, neodymium will have a broader space for utilization.
Post time: Oct-26-2023